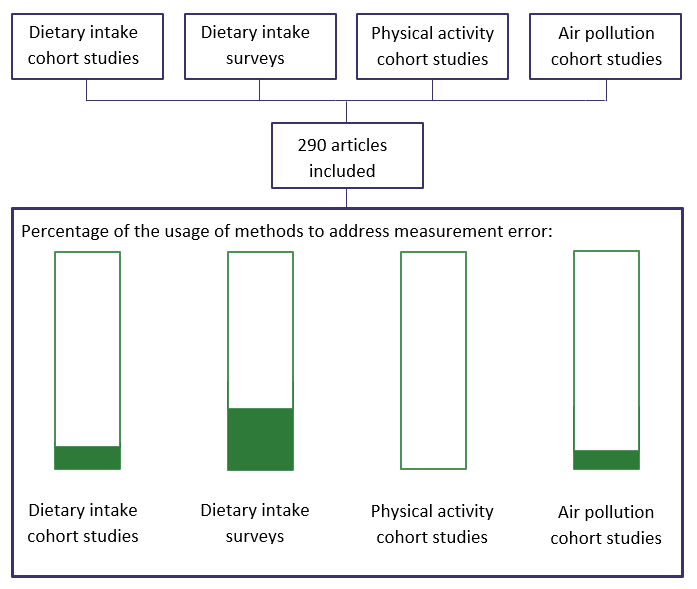
A literature survey of the use of methods to adjust measurement error in four areas of epidemiology revealed that only a minority of published papers present estimates that are adjusted for measurement error:
The following opportunities for improvement have been identified:
Discuss the impact of measurement error on study results.
Discuss the origin, size, structure and potential impact of measurement error.
Consider the impact of dichotomizing a continuous error-prone variable.
Do not naively claim
that random error won´t cause bias in associations,
that attenuation was the only possible direction of bias induced by error,
that categorization reduces the effect of measurement error,
that validated questionnaires don't have bias or
that software is not available.
Mention the influence of adjusting for multiple error-prone exposures on the direction of the bias.
Address all error-prone exposures in your study.
